- Home
- Cosmetic Gynecology
- Clitoral Hood Reduction
Clitoral Hood Reduction - Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery

What is a Clitoral Hood Reduction?
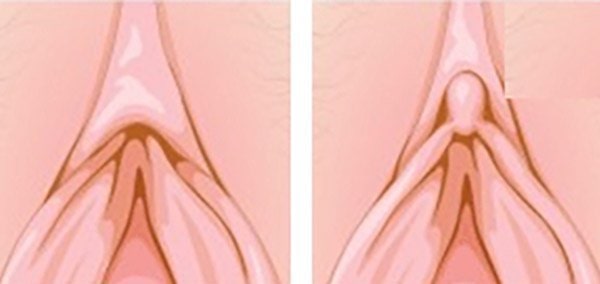
Excess folds of the clitoral hood, or prepuce, can be reduced with a clitoral hood reduction. The procedure is most commonly done along with a labiaplasty.
What does a clitoral hood reduction do?
The extra folds can create a bulge that is exaggerated when the labia minora are reduced, and a clitoral hood reduction can improve the balance in appearance of the female genitalia.
Anesthesia for a clitoral hood reduction
A clitoral hood reduction is usually done at the time of a labiaplasty under either local anesthesia with oral sedation or under general anesthesia.
Clitoral hood reduction procedure
The excess tissue is marked according to the individual’s anatomy. There is a wide variation in the shape and extent of folds. In some patients the excision is performed as a “Y” extension of the labiaplasty. Closure is usually done with absorbable sutures.
What are the risks of a clitoral hood reduction?
There is a risk of bleeding, hematoma, infection, under-resection or over-resection.
Recovering from a clitoral hood reduction
The recovery is primarily determined by the accompanying labiaplasty.
What are the results of a clitoral hood reduction?
In some patients with a heavy clitoral hood, a labiaplasty without a clitoral hood reduction can result in a top-heavy look. A clitoral hood reduction can lend balance to a labiaplasty in such patients. Clitoral hood reduction is generally performed with labiaplasty, which has a high satisfaction rate of over 90 percent.
Recovery Notes
Following a clitoral hood reduction, it is normal for patients to experience some mild swelling, discomfort, or bruising. It is recommended to take 2-3 days off from your daily routine including work and exercise. Resume normal activity as tolerated however refrain from sexual activity for 1 month.
Ideal Candidate
The ideal candidate for a clitoral hood reduction has difficulty stimulating the clitoris or is unhappy with the appearance of the clitoris.
Not Recommended For
Cllitoral hood reduction is not recommended for patients who are seeking to treat Psychosexual dysfunctions such as inability to achieve orgasm or low sex drive.
Side Effects
Side effects from a clitoral hood reduction can include redness, swelling, tenderness, and discharge.
PROS
» Increased Sensation
» Improved Look
» Less Discomfort
CONS
» Infection
» Wound Separation
» Asymmetry

