- Home
- Gynecology Cancers
- Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar Cancer Treatment - Gynecologic Oncology Experts
If you have noticed a lump in your vulva (lips around vagina) that is causing intense itching and pain in the area then it might be a case of cancer of the vulva. Cancer is nothing but the abnormal growth of cells that clump together to form tumors. If the tumor is malignant, the cancer cells metastasize or spread through the blood stream to different parts of the body affecting them.

Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of vulva cancer may include:
» Persistent itching
» Pain and tenderness
» Bleeding but not because of menstruation
» Discoloration
» Skin thickening
» Lump or sores
» Abnormal bleeding
» Burning
Diagnosis
To diagnose the condition the doctor may do a physical examination.
Any abnormality of the vulva can be detected by an examination called as Colposcopy. In this procedure, a device that works like a magnifying glass is used to check for abnormalities.
A procedure called biopsy is done to check for cancer cells in the area. In this procedure, local anesthesia is given in the area and with help of scalpel a part of the affected area is removed for testing. You may need stitches depending on the amount of area removed.
Staging tests are done to determine the stage or extent of your cancer spread. In the staging tests, the doctor examines the pelvis for spread of cancer.
Imaging tests that are done to check chest and abdomen for cancer spread are Computerized Tomography (CT) by which 2D and 3D images of areas are created, X ray, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) which uses magnetic field to produce clear images of organs and Ultrasound that uses high frequency sound waves with help of which images of organs are created.
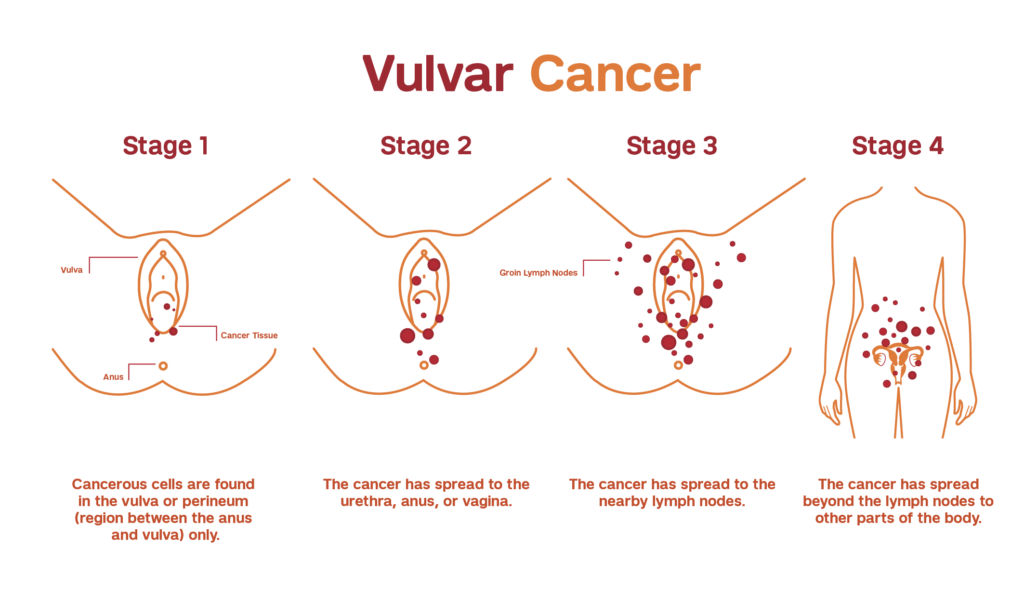
Stages of Vulvar cancer
The stages of vulvar cancer are:
In this stage, the tumor is present on the vulva and there is no spread of cancer to the other parts of body and lymph nodes.
In this stage the tumors spread to the nearby areas like the urethra, anus and vagina.
Lymph nodes are affected by cancer spread.
In this stage, cancer spreads to lymph nodes, bladder, urethra, vagina, rectum and pelvic bone.
In this stage, distant parts of the body are affected by cancer spread.
Treatment
The treatment of vulva cancer depends on the stage of cancer and the general health of the patient. A procedure involving excision or removal of tissue affected with cancer along with a little of normal tissue is done to make sure all cancer cells are removed.
In a surgical procedure called as partial vulvectomy, the affected part of vulva is removed.
In another surgical procedure known as radical vulvectomy, the entire vulva with clitoris and tissues surrounding it are surgically removed.
For severe cancer that has spread to organs beyond vulva, a surgical procedure called Pelvic exenteration is done in which the entire vulva and all organs affected are surgically removed.
If the removal of skin is extensive, reconstructive surgery is done.
The affected lymph nodes are also removed surgically.
Radiation therapy is used in which high power x rays are used to kill cancer cells.
Chemotherapy is also used in combination with radiation therapy in which chemical drugs are given orally or intravenously (through vein).
After treatment regular checkups is a must. The doctor recommends follow up examination twice every year for the first 5 years after treatment.
Prevention
To prevent Vulvar cancer it is important that you practice safe sex. The human papilloma Virus that spreads through sexual transmission can cause vulvar cancer. Hence it is essential to use a condom for protection against HPV virus.
Limiting your sexual partners is also important to reduce exposure to HPV.
Having sex at an early age also increases the risk of HPV infection. It is recommended that you undergo pelvic exams in which vulva is examined for any abnormalities.
Gardasil and Cervarix are two vaccinations that have been developed to give protection against HPV.

